Data analysis simulation
1. Factors that change the signal shape
Parameters such as activation energy, frequency factor (vibration term), number of initial molecules of desorption component, heating rate, etc. change the signal shape and peak temperature. This is clear from the model equation of the temperature programmed desorption method shown below.
Primary surface desorption reaction
![]()
Non-primary surface desorption reaction
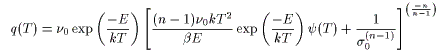
Diffusion desorption
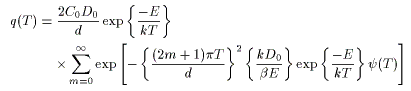
q(T) is the desorption rate, ν0 is the frequency factor, D0 is the vibration term, σ0 is the number of initial molecules, C0 is the initial concentration, n is the reaction order, d is the thickness of the film, E is the activation energy, k is Boltzmann's constant, β is the heating rate, and T is the absolute temperature.
2. Difference by activation energy
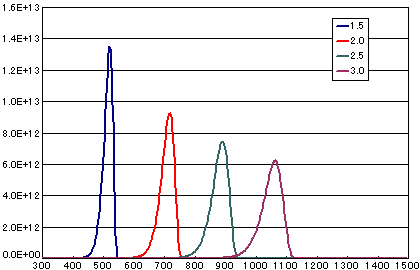
In the case of primary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
|
Frequency factor (sec-1) |
1E13 | 1E13 | 1E13 | 1E13 |
|
Number of initial molecules (molecs./cm2) |
1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
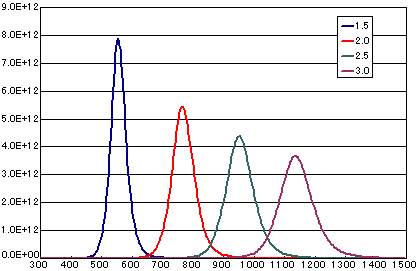
In the case of secondary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
|
Frequency factor (cm2/molesc.sec) |
1E-3 | 1E-3 | 1E-3 | 1E-3 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
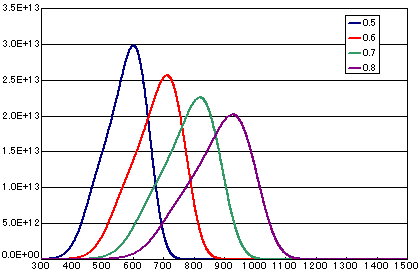
In the case of diffusion limited
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Vibration term(cm2/sec) | 1E-1 | 1E-1 | 1E-1 | 1E-1 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E16 | 1E16 | 1E16 | 1E16 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
3. Difference by frequency factor (vibration term)
In the case of primary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Frequency factor(sec-1) | 1E14 | 1E13 | 1E12 | 1E11 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
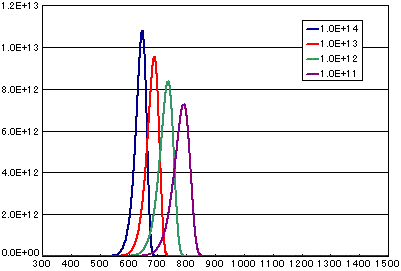
In the case of secondary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Frequency factor(cm2/molecs.sec) | 1E-2 | 1E-3 | 1E-4 | 1E-5 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
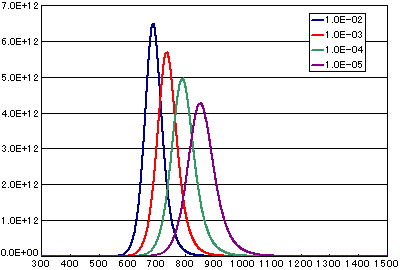
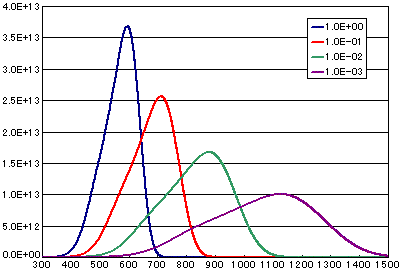
In the case of diffusion limited
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Vibration term(cm2/sec) | 1E-0 | 1E-1 | 1E-2 | 1E-3 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E16 | 1E16 | 1E16 | 1E16 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
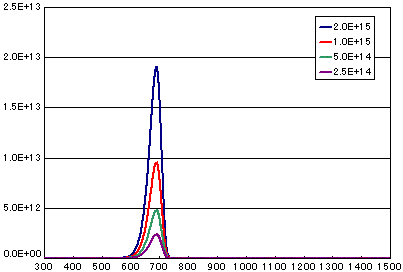
4. Difference by number of initial molecules
In the case of primary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Frequency factor(sec-1) | 1E13 | 1E13 | 1E13 | 1E13 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 2E15 | 1E15 | 5E14 | 2.5E14 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
0.5 |
In the case of secondary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Frequency factor(cm2/molecs.sec) | 1E-3 | 1E-3 | 1E-3 | 1E-3 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 2E15 | 1E15 | 5E14 | 2.5E14 |
|
Heating rate(K/sec) |
0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
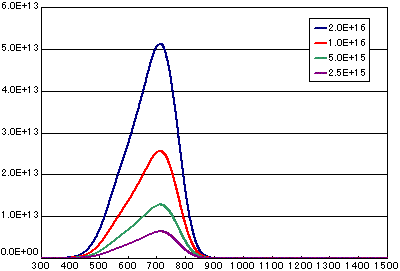
In the case of diffusion limited
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Frequency factor(cm2/sec) | 1E-1 | 1E-1 | 1E-1 | 1E-1 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 2E16 | 1E16 | 5E15 | 2.5E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
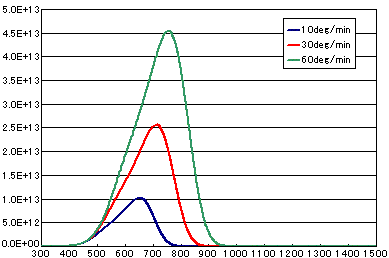
5. Difference by heating rate
In the case of primary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Frequency factor(sec-1) | 1E13 | 1E13 | 1E13 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 1/6 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
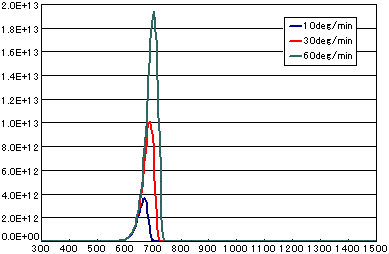
In the case of secondary elimination reaction
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Frequency factor(cm2/molecs.sec) | 1E-3 | 1E-3 | 1E-3 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E15 | 1E15 | 1E15 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 1/6 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
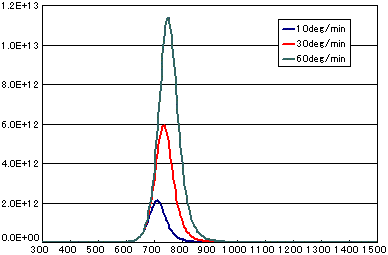
In the case of diffusion limited
| A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activation energy(eV) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Vibration term(cm2/sec) | 1E-1 | 1E-1 | 1E-1 |
| Number of initial molecules(molecs./cm2) | 1E16 | 1E16 | 1E16 |
| Heating rate(K/sec) | 1/6 | 0.5 | 1.0 |